What is “abstract” in Java?
Abstract is a non-access modifier in Java that is used to declare classes, methods, and interfaces that cannot be instantiated directly. An abstract class or method must be extended or implemented by a subclass before it can be used.
What is Abstraction in Java? Why is it important in software development?
Abstraction is a concept in software development that refers to the ability to hide implementation details and provide a simple, high-level interface for interacting with a system.
It is important in software development because:
-it allows us to manage complexity by breaking down a system into smaller, more manageable parts.
-allows us to create reusable code,
-design software that is modular, extensible, and maintainable.
How to achieve or implement Abstraction in Java?
Abstraction can be achieved in Java through the use of abstract classes and interfaces.
a) An abstract class is a class that cannot be instantiated directly and must be extended by a subclass.
b) An interface is a collection of abstract methods that must be implemented by any class that implements the interface.
What is Abstract class in Java? How to define it?
An abstract class in Java is a class that is declared with the “abstract” keyword and cannot be instantiated directly.
Abstract classes are used to define a common interface for a group of subclasses, while allowing each subclass to implement its own behavior. To define an abstract class in Java, you simply use the “abstract” keyword in the class declaration, like this:
public abstract class MyClass {
// abstract methods and other members here
}Any class that extends an abstract class must implement any abstract methods that are defined in the abstract class.
syntax:
accessmodifier abstract class <classname>{
variables;
abstract methods();
concretemethods(){logic inside}
constructors(){l+s;}
}
public abstract class GraphicObject {
// declare fields
// declare nonabstract methods
abstract void draw();
}
When an abstract class is subclassed, the subclass usually provides implementations for all of the abstract methods in its parent class. However, if it does not, then the s
Abstract classes are similar to interfaces. You cannot instantiate them, and they may contain a mix of methods declared with or without an implementation. However, with abstract classes, you can declare fields that are not static and final, and define public, protected, and private concrete methods.AbstractMap, which is part of the Collections Framework. Its subclasses (which include HashMap, TreeMap, and ConcurrentHashMap) share many methods (including get, put, isEmpty, containsKey, and containsValue) that AbstractMap defines.partial abstraction can be achieved through abstract class
- Consider using abstract classes if any of these statements apply to your situation:
- You want to share code among several closely related classes.
- You expect that classes that extend your abstract class have many common methods or fields, or require access modifiers other than public (such as protected and private).
- You want to declare non-static or non-final fields. This enables you to define methods that can access and modify the state of the object to which they belong.
With the basics of Abstraction being covered, now let’s begin with the questions.
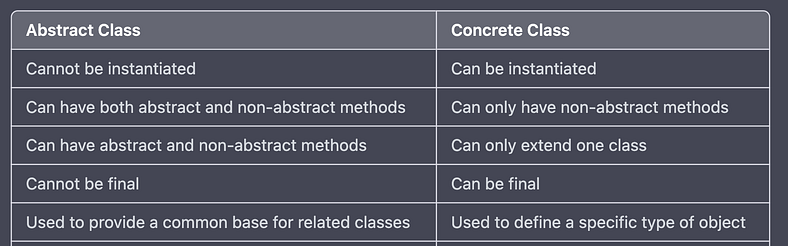
1.What is the difference between abstract class and concrete class?
2. What is Abstract method in Java?
A method which is declared with abstract modifier and has no implementation (means no body) is called abstract method in java.
It does not contain any body. It has simply a signature declaration followed by a semicolon. It has the following general form as given below.
Syntax:
abstract type MethodName(arguments); // No bodyFor example:
abstract void message(); // No body.abstract void methodname();
abstract void methodname(datatype p1);
abstract datatype methodname(datatype p1);
abstract void moveTo(double deltaX, double deltaY);
3. Can an abstract method be declared as static? Why?
No, an abstract method cannot be declared as static in Java.
This is because abstract methods are designed to be overridden by subclasses, and static methods are not subject to overriding.
Static methods belong to the class itself, rather than to any particular instance of the class, and can be called without creating an instance of the class.
However, abstract methods must be implemented by subclasses, and so they require an instance of the subclass to be created in order to be used.
Therefore, since static methods and abstract methods serve different purposes, it is not possible to declare an abstract method as static.
4. Can an abstract method be declared with private modifier?
No, it cannot be private because the abstract method must be implemented in the child class.
If we declare it as private, we cannot implement it from outside the class.
5. When to use Abstract class in Java? Illustrate with examples.
Abstract classes in Java are useful when you want to define a common interface for a group of related classes, while allowing each subclass to provide its own implementation. Here are a few situations where you might want to use an abstract class:
When you have a group of related classes that share some common behavior, but also have some unique behavior that cannot be generalized. In this case, you can define the common behavior in the abstract class, and leave the unique behavior to be implemented by the subclasses.
Example —
Suppose you are building a game that has different types of characters, such as warriors, mages, and archers. Each character has some common attributes and behavior, such as health points and the ability to move, but they also have unique behavior, such as different types of attacks or spells. In this case, you could define an abstract class called “Character” that provides the common behavior and attributes, and leave the unique behavior to be implemented by the subclasses.
public abstract class Character {
protected int health;
protected int x;
protected int y;
public Character(int health, int x, int y) {
this.health = health;
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public void move(int deltaX, int deltaY) {
x += deltaX;
y += deltaY;
}
public abstract void attack();
}When you want to enforce certain rules or contracts that all subclasses must follow. By defining abstract methods in the abstract class, you can ensure that all subclasses provide an implementation for those methods.
Example-
Suppose you are building a payment processing system, and you have different types of payment methods, such as credit cards, PayPal, and wire transfers.
Each payment method has some common behavior, such as validating the payment details and charging the customer, but they also have some unique behavior, such as the API calls to external payment gateways. In this case, you could define an abstract class called “PaymentMethod” that provides the common behavior and attributes, and enforces the contract that all payment methods must implement a certain set of methods.
public abstract class PaymentMethod {
protected String paymentId;
protected double amount;
protected String currency;
public PaymentMethod(String paymentId, double amount, String currency) {
this.paymentId = paymentId;
this.amount = amount;
this.currency = currency;
}
public boolean validatePayment() {
// Validate the payment details, such as the amount, currency, and payment ID
return true;
}
public abstract void chargeCustomer();
public abstract void refundCustomer();
}
In this example, the abstract class “PaymentMethod” defines the common attributes and behavior for all payment methods, such as validating the payment details and charging the customer, and enforces the contract that all payment methods must implement the “chargeCustomer” and “refundCustomer” methods.
Each subclass of PaymentMethod, such as “CreditCard”, “PayPal”, and “WireTransfer”, would provide its own implementation of the “chargeCustomer” and “refundCustomer” methods, while inheriting the common behavior and attributes from the abstract class. This ensures that all payment methods follow the same contract and can be used interchangeably in the payment processing system.
6. When to use Abstract method in Java?
An abstract method can be used when:
a) When the same method has to perform different tasks depending on the object calling it.
b) When you need to be overridden in its non-abstract subclasses.
7.Can an abstract class have constructor? Why?
Yes, an abstract class can have a constructor in Java.
A constructor is a special method that is used to initialize the state of an object when it is created.
Even though an abstract class cannot be instantiated directly, it can still be used as a superclass for its concrete subclasses, which can be instantiated.
When a subclass object is created, the constructor of the superclass is called to initialize the common attributes inherited from the superclass. Therefore, an abstract class may need to have a constructor to initialize these common attributes, which will be inherited by its subclasses.
Example:
public abstract class Shape {
protected int x;
protected int y;
public Shape(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public abstract void draw();
}8.Is it possible to achieve multiple inheritance through abstract class? Why?
Yes, it is possible to achieve multiple inheritance through abstract class in Java. This is because an abstract class can implement multiple interfaces, and each of these interfaces can have its own set of methods that must be implemented by the abstract class.
By doing so, the abstract class can inherit functionality from multiple sources, effectively achieving multiple inheritance.
However, it is important to note that Java does not support multiple inheritance of classes, which means that a class cannot extend more than one class. This is because multiple inheritance of classes can lead to the diamond problem, where the same method is inherited from two different parent classes, leading to ambiguity in the implementation.
By using abstract classes and interfaces, Java provides a way to achieve some of the benefits of multiple inheritance, while avoiding the problems that can arise from multiple inheritance of classes.
9. What is the difference between Abstraction and Encapsulation?
Abstraction and encapsulation are related concepts, but they are not the same thing.
Abstraction is the process of hiding implementation details, while encapsulation is the process of hiding data or implementation details within a class.
Abstraction is a more general concept, while encapsulation is a more specific one.
In other words, abstraction is a way to manage complexity, while encapsulation is a way to protect data.
10. Can we instantiate a class which does not have even a single abstract methods but declared as abstract?
No, We can’t instantiate a class once it is declared as abstract even though it does not have abstract methods.
11. Why final and abstract can not be used at a time?
Because, final and abstract are totally opposite in nature.
A final class or method can not be modified further where as abstract class or method must be modified further.
“final” keyword is used to denote that a class or method does not need further improvements.
“abstract” keyword is used to denote that a class or method needs further improvements.
12.What are some common design patterns that make use of abstraction?
There are many design patterns that make use of abstraction, including the Factory Pattern, the Strategy Pattern, and the Observer Pattern. These patterns all make use of interfaces or abstract classes to define a common set of methods that can be implemented by multiple classes.
13. What are the advantages and disadvantages of using abstraction in software development?
The advantages of using abstraction in software development include:
improved code reuse
increased modularity
and improved maintainability
The disadvantages of using abstraction include:
increased complexity and overhead
potential for over-engineering
14. What are some best practices for using abstraction in your code?
Some best practices for using abstraction in your code include:
defining clear and concise interfaces or abstract classes
avoiding over-engineering,
favoring composition over inheritance.
Additionally, it is important to test your classes and interfaces thoroughly to ensure that they are working as intended.
By mastering the art of abstraction, you can create efficient and organized programs, improve the readability and maintainability of your code, and facilitate collaboration with other developers. The expert-recommended questions on abstraction provided in this article serve as a valuable resource for Java developers who want to deepen their understanding of the topic and prepare for interviews. With sufficient practice and preparation, you can confidently approach Java OOP interviews and demonstrate your expertise in abstraction.
===============================================
Interface: In the Java programming language, an interface is a reference type, similar to a class, that can contain only constants, method signatures, default methods, static methods, and nested types. Method bodies exist only for default methods and static methods. Interfaces cannot be instantiated—they can only be implemented by classes or extended by other interfaces..
Since Java 8, we can have default and static methods in an interface.
Since Java 9, we can have private methods in an interface.
Why use Java interface?
It is used to achieve abstraction
By interface, we can support the functionality of multiple inheritance
How to declare an interface?
An interface is declared by using the interface keyword.
The interface body can contain abstract methods, default methods, and static methods. An abstract method within an interface is followed by a semicolon, but no braces (an abstract method does not contain an implementation).
default modifier, and static methods with the static keyword. All abstract, default, and static methods in an interface are implicitly public, so you can omit the public modifier.- Consider using interfaces if any of these statements apply to your situation:
- You expect that unrelated classes would implement your interface. For example, the interfaces
ComparableandCloneableare implemented by many unrelated classes. - You want to specify the behavior of a particular data type, but not concerned about who implements its behavior.
- You want to take advantage of multiple inheritance of type.
- You expect that unrelated classes would implement your interface. For example, the interfaces
HashMap, which implements the interfaces Serializable, Cloneable, and Map<K, V>interface syntax:
accessmodifier interface <interfacename>{
int WORDS=200; // public static final int WORDS=200;
//abstract methods
abstract methods(); //public abstract returntype methodname();
//default methods starts with default keyword
default void methodname(){l+s}
//static methods
static void methodname(){l+s}
}
naming conventions:everyword first letter should be capital
class classname implements interfacename{
}
ex:
public class FirefoxDriver implements WebDriver{}
how can you map interface and implementing class
interfacename refvar=new implementingclass();
//how can you call the methods
refvar.methodname();
how can you call return type nonstatic method?
rettype variable=objectreference.nonstaticmethod();
What is Marker or tagged interface?
An Interface which has no member is known as a marker or tagged interface.
ex:
accessmodifier interface interfacename{
}
Functional Interface:it has only one abstract method and any number of default methods.
@FunctionalInterface
public interface interfacename{
one abstarctmethod();
many defaultmethods();
}
Example:
package ooops;
public interface Shape {
int MAX_COUNT=100;
void area();
void draw();
void print();
}
------------------------------------
package ooops;
public class Circle implements Shape {
public void draw(){
System.out.println("draw the circle");
}
public void area(){
int r=30;
double area=3.1415*r*r;
System.out.println("area of the circle:"+area);
}
@Override
public void print() {
System.out.println("print the circle");
}
}
-----------------------------------------
package ooops;
public class Rectangle implements Shape{
@Override
public void area() {
int w=10,l=20;
int area=w*l;
System.out.println("the area of the rectangle:"+area);
}
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("draw the rectangle");
}
@Override
public void print() {
System.out.println("print the rectangle");
}
}
-------------------------------------------------
package ooops;
public class InterfaceDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//interface refevar=new implementingclass();
Shape s=new Rectangle();
//refe.methodname();
s.area();
s.draw();
s.print();
}
}
----------------------------------------
========================================================
java supports multiple inheritance incase of interface
you can extend mutliple interfaces to another interface.
interface Printable{
print();
msg();
}
interface Runnable{
run();
}
interface Showable extends Printable,Runnable{
show();
}
class A implements Showable{
}
Relationship Between Class and Interface
- A class can extend another class using extends keyword.
- A class can implement an interface using the implements keyword.
- An interface can extend another interface using extends keyword. It cannot extend a class.

A class can implement one or more interface and an interface can extend one or more interface.

Difference between abstract class and interface
Abstract class
|
Interface
|
1) Abstract class can have abstract and non-abstract methods.
|
Interface can have only abstract methods. Since Java 8, it can have default and static methods also.
|
2) Abstract class doesn't support multiple inheritance.
|
Interface supports multiple inheritance.
|
3) Abstract class can have final, non-final, static and
non-static variables.
|
Interface has only static and final variables.
|
4) Abstract class can provide the implementation of an interface.
|
Interface can't provide the implementation of an abstract class.
|
5) The abstract keyword is used to declare an abstract class.
|
The interface keyword is used to declare the interface.
|
6) An abstract class can extend another Java class and implement multiple Java
interfaces.
|
An interface can extend another Java interface only.
|
7) An abstract class can be extended using the keyword "extends".
|
An interface can be implemented in the class using the keyword "implements".
|
8) A Java abstract class can have class members like private, protected, etc.
|
Members of a Java interface are public by
default.
|
9)Example:
public abstract class Shape{ public abstract void draw(); } |
Example:
public interface Drawable{ void draw(); } |


No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.