1. Write a program to print numbers from 1 to 10.
public class PrintNumbers { public static void main(String[] args) { for(int i=1; i<=10; i++) { System.out.println(i); } } }
2.Write a program to calculate the sum of first 10 natural number.
public class SumNumbers { public static void main(String[] args) { int sum = 0; for(int i=1; i<=10; i++) { sum += i; } System.out.println("Sum: " + sum); } }
3.Write a program that prompts the user to input a positive integer. It should then print the multiplication table of that number.
import java.util.Scanner; public class Table { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in); int num; System.out.print("Enter any positive integer: "); num = console.nextInt(); System.out.println("Multiplication Table of " + num); for(int i=1; i<=10; i++) { System.out.println(num +" x " + i + " = " + (num*i) ); } } }
4.Write a program to find the factorial value of any number entered through the keyboard.
import java.util.Scanner; public class FactorialDemo1 { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in); int num; // To hold number int fact = 1; // To hold factorial System.out.print("Enter any positive integer: "); num = console.nextInt(); for(int i=1; i<=num; i++) { fact *= i; } System.out.println("Factorial: "+ fact); } }
5.
Two numbers are entered through the keyboard. Write a program to find the value of one number raised to the power of another. (Do not use Java built-in method)
import java.util.Scanner; public class PowerDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in); int base; int power; int result = 1; System.out.print("Enter the base number "); base = console.nextInt(); System.out.print("Enter the power "); power = console.nextInt(); for(int i = 1; i <= power; i++) { result *= base; } System.out.println("Result: "+ result); } }
6.
Write a program that prompts the user to input an integer and then outputs the number with the digits reversed. For example, if the input is 12345, the output should be 54321.
import java.util.Scanner; public class ReverseNumber { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in); int number; int reverse = 0; System.out.print("Enter the number "); number = console.nextInt(); int temp = number; int remainder = 0; while(temp>0) { remainder = temp % 10; reverse = reverse * 10 + remainder; temp /= 10; } System.out.println("Reverse of " + number + " is " + reverse); } }
7.
Write a program that reads a set of integers, and then prints the sum of the even and odd integers.
import java.util.Scanner; public class ReadSetIntegers { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in); int number; char choice; int evenSum = 0; int oddSum = 0; do { System.out.print("Enter the number "); number = console.nextInt(); if( number % 2 == 0) { evenSum += number; } else { oddSum += number; } System.out.print("Do you want to continue y/n? "); choice = console.next().charAt(0); }while(choice=='y' || choice == 'Y'); System.out.println("Sum of even numbers: " + evenSum); System.out.println("Sum of odd numbers: " + oddSum); } }
8.Write a program that prompts the user to input a positive integer. It should then output a message indicating whether the number is a prime number.
import java.util.Scanner; public class TestPrime { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in); int number; System.out.print("Enter the positive integer "); number = console.nextInt(); boolean flag = true; for(int i = 2; i < number; i++) { if(number % i == 0) { flag = false; break; } } if(flag && number > 1) { System.out.println("Number is prime"); } else { System.out.println("Number is not prime"); } } }
9.
Write a do-while loop that asks the user to enter two numbers. The numbers should be added and the sum displayed. The loop should ask the user whether he or she wishes to perform the operation again. If so, the loop should repeat; otherwise it should terminate.
import java.util.Scanner; public class SumAgain { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in); int number1, number2; char choice; do { System.out.print("Enter the first number "); number1 = console.nextInt(); System.out.print("Enter the second number "); number2 = console.nextInt(); int sum = number1 + number2; System.out.println("Sum of numbers: " + sum); System.out.print("Do you want to continue y/n? "); choice = console.next().charAt(0); System.out.println(); }while(choice=='y' || choice == 'Y'); } }
10.
Write a program to enter the numbers till the user wants and at the end it should display the count of positive, negative and zeros entered.
import java.util.Scanner; public class CountNumbers { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in); int number, countPositive = 0, countNegative = 0, countZero = 0; char choice; do { System.out.print("Enter the number "); number = console.nextInt(); if(number > 0) { countPositive++; } else if(number < 0) { countNegative++; } else { countZero++; } System.out.print("Do you want to continue y/n? "); choice = console.next().charAt(0); }while(choice=='y' || choice == 'Y'); System.out.println("Positive numbers: " + countPositive); System.out.println("Negative numbers: " + countNegative); System.out.println("Zero numbers: " + countZero); } }
11. Write a program to enter the numbers till the user wants and at the end the program should display the largest and smallest numbers entered.
import java.util.Scanner; public class FindMaxMin { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in); int number; int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE; // Intialize max with minimum value int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // Intialize min with maximum value char choice; do { System.out.print("Enter the number "); number = console.nextInt(); if(number > max) { max = number; } if(number < min) { min = number; } System.out.print("Do you want to continue y/n? "); choice = console.next().charAt(0); }while(choice=='y' || choice == 'Y'); System.out.println("Largest number: " + max); System.out.println("Smallest number: " + min); } }
12. Write a program to print Fibonacci series of n terms where n is input by user :
0 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 24 ....
15. Write a java program to check Armstrong number.
Average: ?(n^2)
Worst: O(n^2)
public class PrintNumbers { public static void main(String[] args) { for(int i=1; i<=10; i++) { System.out.println(i); } } }
2.Write a program to calculate the sum of first 10 natural number.
public class SumNumbers { public static void main(String[] args) { int sum = 0; for(int i=1; i<=10; i++) { sum += i; } System.out.println("Sum: " + sum); } }
3.Write a program that prompts the user to input a positive integer. It should then print the multiplication table of that number.
import java.util.Scanner; public class Table { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in); int num; System.out.print("Enter any positive integer: "); num = console.nextInt(); System.out.println("Multiplication Table of " + num); for(int i=1; i<=10; i++) { System.out.println(num +" x " + i + " = " + (num*i) ); } } }
4.Write a program to find the factorial value of any number entered through the keyboard.
import java.util.Scanner; public class FactorialDemo1 { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in); int num; // To hold number int fact = 1; // To hold factorial System.out.print("Enter any positive integer: "); num = console.nextInt(); for(int i=1; i<=num; i++) { fact *= i; } System.out.println("Factorial: "+ fact); } }
5.
Two numbers are entered through the keyboard. Write a program to find the value of one number raised to the power of another. (Do not use Java built-in method)
import java.util.Scanner; public class PowerDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in); int base; int power; int result = 1; System.out.print("Enter the base number "); base = console.nextInt(); System.out.print("Enter the power "); power = console.nextInt(); for(int i = 1; i <= power; i++) { result *= base; } System.out.println("Result: "+ result); } }
6.
Write a program that prompts the user to input an integer and then outputs the number with the digits reversed. For example, if the input is 12345, the output should be 54321.
import java.util.Scanner; public class ReverseNumber { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in); int number; int reverse = 0; System.out.print("Enter the number "); number = console.nextInt(); int temp = number; int remainder = 0; while(temp>0) { remainder = temp % 10; reverse = reverse * 10 + remainder; temp /= 10; } System.out.println("Reverse of " + number + " is " + reverse); } }
7.
Write a program that reads a set of integers, and then prints the sum of the even and odd integers.
import java.util.Scanner; public class ReadSetIntegers { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in); int number; char choice; int evenSum = 0; int oddSum = 0; do { System.out.print("Enter the number "); number = console.nextInt(); if( number % 2 == 0) { evenSum += number; } else { oddSum += number; } System.out.print("Do you want to continue y/n? "); choice = console.next().charAt(0); }while(choice=='y' || choice == 'Y'); System.out.println("Sum of even numbers: " + evenSum); System.out.println("Sum of odd numbers: " + oddSum); } }
8.Write a program that prompts the user to input a positive integer. It should then output a message indicating whether the number is a prime number.
import java.util.Scanner; public class TestPrime { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in); int number; System.out.print("Enter the positive integer "); number = console.nextInt(); boolean flag = true; for(int i = 2; i < number; i++) { if(number % i == 0) { flag = false; break; } } if(flag && number > 1) { System.out.println("Number is prime"); } else { System.out.println("Number is not prime"); } } }
9.
Write a do-while loop that asks the user to enter two numbers. The numbers should be added and the sum displayed. The loop should ask the user whether he or she wishes to perform the operation again. If so, the loop should repeat; otherwise it should terminate.
import java.util.Scanner; public class SumAgain { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in); int number1, number2; char choice; do { System.out.print("Enter the first number "); number1 = console.nextInt(); System.out.print("Enter the second number "); number2 = console.nextInt(); int sum = number1 + number2; System.out.println("Sum of numbers: " + sum); System.out.print("Do you want to continue y/n? "); choice = console.next().charAt(0); System.out.println(); }while(choice=='y' || choice == 'Y'); } }
10.
Write a program to enter the numbers till the user wants and at the end it should display the count of positive, negative and zeros entered.
import java.util.Scanner; public class CountNumbers { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in); int number, countPositive = 0, countNegative = 0, countZero = 0; char choice; do { System.out.print("Enter the number "); number = console.nextInt(); if(number > 0) { countPositive++; } else if(number < 0) { countNegative++; } else { countZero++; } System.out.print("Do you want to continue y/n? "); choice = console.next().charAt(0); }while(choice=='y' || choice == 'Y'); System.out.println("Positive numbers: " + countPositive); System.out.println("Negative numbers: " + countNegative); System.out.println("Zero numbers: " + countZero); } }
11. Write a program to enter the numbers till the user wants and at the end the program should display the largest and smallest numbers entered.
import java.util.Scanner; public class FindMaxMin { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in); int number; int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE; // Intialize max with minimum value int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // Intialize min with maximum value char choice; do { System.out.print("Enter the number "); number = console.nextInt(); if(number > max) { max = number; } if(number < min) { min = number; } System.out.print("Do you want to continue y/n? "); choice = console.next().charAt(0); }while(choice=='y' || choice == 'Y'); System.out.println("Largest number: " + max); System.out.println("Smallest number: " + min); } }
12. Write a program to print Fibonacci series of n terms where n is input by user :
0 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 24 ....
import java.util.Scanner;
public class FibonacciSeries
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in);
int number; // To hold number of terms
int firstTerm = 0,
secondTerm = 1,
thirdTerm;
System.out.print("Enter number of terms of series : ");
number = console.nextInt();
System.out.print(firstTerm + " " + secondTerm + " ");
for(int i = 3; i <= number; i++)
{
thirdTerm = firstTerm + secondTerm;
System.out.print(thirdTerm + " ");
firstTerm = secondTerm;
secondTerm = thirdTerm;
}
}
}
13.Write a program that generates a random number and asks the user to guess what the number is. If the user's guess is higher than the random number, the program should display "Too high, try again." If the user's guess is lower than the random number, the program should display "Too low, try again." The program should use a loop that repeats until the user correctly guesses the random number.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class GuessMyNumber
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in);
int number, // To hold the random number
guess, // To hold the number guessed by user
tries = 0; // To hold number of tries
number = (int) (Math.random() * 100) + 1; // get random number between 1 and 100
System.out.println("Guess My Number Game");
System.out.println();
do
{
System.out.print("Enter a guess between 1 and 100 : ");
guess = console.nextInt();
tries++;
if (guess > number)
{
System.out.println("Too high! Try Again");
}
else if (guess < number)
{
System.out.println("Too low! Try Again");
}
else
{
System.out.println("Correct! You got it in " + tries + " guesses!");
}
}while (guess != number);
}
}
14.Write a java program to check palindrome number.
Palindrome number in java: A palindrome number is a number that is same after reverse. For example 545, 151, 34543, 343, 171, 48984 are the palindrome numbers. It can also be a string like LOL, MADAM etc.
Palindrome number algorithm
- Get the number to check for palindrome
- Hold the number in temporary variable
- Reverse the number
- Compare the temporary number with reversed number
- If both numbers are same, print "palindrome number"
- Else print "not palindrome number"
- class PalindromeExample{
- public static void main(String args[]){
- int r,sum=0,temp;
- int n=454;//It is the number variable to be checked for palindrome
- temp=n;
- while(n>0){
- r=n%10; //getting remainder
- sum=(sum*10)+r;
- n=n/10;
- }
- if(temp==sum)
- System.out.println("palindrome number ");
- else
- System.out.println("not palindrome");
- }
- }
Let's write a java program to check whether the given number is armstrong number or not.
Armstrong Number in Java: A positive number is called armstrong number if it is equal to the sum of cubes of its digits for example 0, 1, 153, 370, 371, 407 etc.
Let's try to understand why 153 is an Armstrong number.
Let's try to understand why 371 is an Armstrong number.
- class ArmstrongExample{
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int c=0,a,temp;
- int n=153;//It is the number to check armstrong
- temp=n;
- while(n>0)
- {
- a=n%10;
- n=n/10;
- c=c+(a*a*a);
- }
- if(temp==c)
- System.out.println("armstrong number");
- else
- System.out.println("Not armstrong number");
- }
- }
====================================================
Check given number is neon number or not?
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* write a program to check given number is neon or not
* neon number:square the given input, then sum all the digits in that number, then if you get same as initial number then that number is called neon number
* int n=9 sqrval=n*n=81
* sum=1+8=>9
* @param n
*/
protected static void checkGivenNumberIsNeon(int n) {
//step declare all the variables
int rem,sum=0;
//step2 -square the given input
int sqrval=n*n;
//step3 - loop to get each digit from the sqrval
while(sqrval>0) {
//step4-extract each digit from the sqrval using %
rem=sqrval%10;
sum=sum + rem;
sqrval=sqrval/10;
}
if(n==sum) {
System.out.println("given number: "+ n + " is a neon number: "+sum );
}else {
System.out.println("given number: "+n+ " is not a neon number: "+sum );
}
}
===========================================================
Write a program to print pyramyd shape
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* write a program to print the pyramid shape
* *
* * *
* * * *
* * * * *
* * * * * *
*
*/
public static void printPyramidShape() {
//create object Scanner class
Scanner scobj=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Please enter no of rows you want in pyramid shape:");
int noOfRows=scobj.nextInt();
//initialize the rowcount with 1
int rowCount=1;
for(int i=noOfRows;i>0;i--) {
//print i spaces
for(int j=0;j<=i;j++) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
for(int k=1;k<=rowCount;k++) {
//System.out.print(" * ");
//System.out.print(rowCount+" ");
System.out.print(" 1 ");
}
System.out.println();
//increment the rowCount by 1
rowCount++;
}
}
===============================================================
Extract maximum numeric value from a given string
iven an alphanumeric string, extract maximum numeric value from that string. Examples:
Input : 100klh564abc365bg Output : 564 Maximum numeric value among 100, 564 and 365 is 564. Input : abchsd0365sdhs Output : 365
===================
// Java regex program to extract the maximum value import java.util.regex.Matcher; import java.util.regex.Pattern; class GFG { // Method to extract the maximum value static int extractMaximum(String str) { // regular expression for atleast one numeric digit String regex = "\\d+"; // compiling regex Pattern p = Pattern.compile(regex); // Matcher object Matcher m = p.matcher(str); // initialize MAX = 0 int MAX = 0; // loop over matcher while(m.find()) { // convert numeric string to integer int num = Integer.parseInt(m.group()); // compare num with MAX, update MAX if num > MAX if(num > MAX) MAX = num; } return MAX; } public static void main (String[] args) { String str = "100klh564abc365bg"; System.out.println(extractMaximum(str)); } }
Approach 2)public class ExtractMaxNumFromString{==============================================================
Write a program to find First char which is reoccurred:
package interviewprograms;
public class FirstCharReoccurred {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s="BCDDB";
int len=s.length();
//iterate the string
for(int i=0;i<len;i++) {
if(s.substring(i+1, len).contains(s.substring(i, i+1))) {
System.out.println("First char which is reoccurred:"+(s.substring(i, i+1)));
break;
}
}
}
}
==============================================================
Write a program to find first re-occurred char
package interviewprograms;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class FirstCharReoccurred {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s="BCDDB";
Set<String>charSet=new HashSet<>();
int len=s.length();
//iterate the string
for(int i=0;i<len;i++) {
boolean isAdded=charSet.add(s.substring(i, i+1));
if(!isAdded) {
System.out.println("First reoccurred char is:"+(s.substring(i, i+1)));
break;
}
}
}
}
===============================================================================================
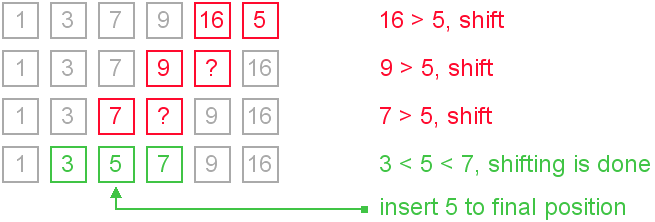
16. Write a java program to sort an array elements using bubble sort algorithm.
We can create a java program to sort array elements using bubble sort. Bubble sort algorithm is known as the simplest sorting algorithm.
In bubble sort algorithm, array is traversed from first element to last element. Here, current element is compared with the next element. If current element is greater than the next element, it is swapped.
- public class BubbleSortExample {
- static void bubbleSort(int[] arr) {
- int n = arr.length;
- int temp = 0;
- for(int i=0; i < n; i++){
- for(int j=1; j < (n-i); j++){
- if(arr[j-1] > arr[j]){
- //swap elements
- temp = arr[j-1];
- arr[j-1] = arr[j];
- arr[j] = temp;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- int arr[] ={3,60,35,2,45,320,5};
- System.out.println("Array Before Bubble Sort");
- for(int i=0; i < arr.length; i++){
- System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
- }
- System.out.println();
- bubbleSort(arr);//sorting array elements using bubble sort
- System.out.println("Array After Bubble Sort");
- for(int i=0; i < arr.length; i++){
- System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
- }
- }
- }
- Output:
Array Before Bubble Sort 3 60 35 2 45 320 5 Array After Bubble Sort 2 3 5 35 45 60 320
17.
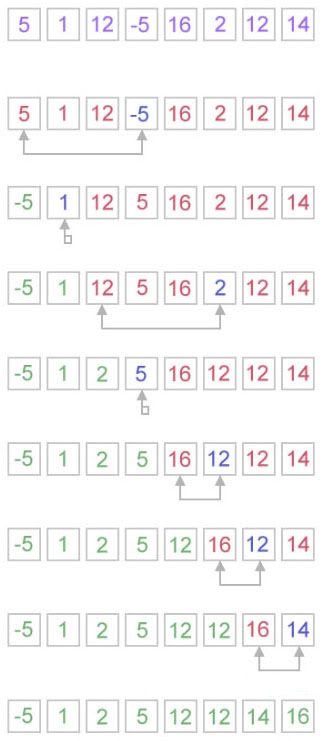
Selection Sort in Java
We can create a java program to sort array elements using selection sort. In selection sort algorithm, we search for the lowest element and arrange it to the proper location. We swap the current element with the next lowest number.

How does selection sort work?
The selection sort algorithm works in a very simple way. It maintains two subarray for the given array.
- The subarray is already sorted.
- And the second subarray is unsorted.
With every iteration of selection sort, an element is picked from the unsorted subarray and moved to the sorted subarray.
Time Complexity
Best: ?(n^2)Average: ?(n^2)
Worst: O(n^2)
Space Complexity
O(1)Selection Sort Java Example
Output:
Before Selection Sort 9 14 3 2 43 11 58 22 After Selection Sort 2 3 9 11 14 22 43 58
Selection Sort in Java (Another way)
You can also use a method where array is not predefined. Here, user has to put the elements as input.
In the following Java program, we ask user to enter the array elements or number, now compare the array's element and start swapping with the variable temp. Put the first element in the temp and the second element in the first, and then temp in the second number and continue for the next match to sort the whole array in ascending order.

No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.