a) Declare an array numArray of 15 elements of type int.
b) Output the value of the tenth element of the array alpha.
c) Set the value of the fifth element of the array alpha to 35.
d) Set the value of the ninth element of the array alpha to the sum of the sixth and thirteenth elements of the array alpha.
//Declare an array numArray of 15 elements of type int
int[] numArray = new int[15];
//Output the value of the tenth element of the array alpha.
System.out.println(alpha[9]);
//Set the value of the fifth element of the array alpha to 35.
alpha[4] = 35;
//Set the value of the ninth element of the array alpha to the sum of
//the sixth and thirteenth elements of the array alpha
alpha[8] = alpha[5] + alpha[12];
"Sunday", "Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday", "Thursday", "Friday" and "Saturday".
b) Write a loop that displays the contents of each element in the array that you declared.
// Declare a string array and initialize
String[] days = {"Sunday", "Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday", "Thursday", "Friday" , "Saturday"};
// Displays the contents of each element
for (String day : days)
{
System.out.println(day);
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ArraySum
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
final int SIZE = 10;
// Create an array to hold numbers.
int[] numbers = new int[SIZE];
Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter " + SIZE + " numbers.");
// Get employees' salary.
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++)
{
numbers[i] = console.nextInt();
}
int sum = 0;
// Calculate the sum.
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++)
{
sum += numbers[i];
}
System.out.println("Sum of numbers: " + sum);
}
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ArrayCopy
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
final int SIZE = 5;
int[] list1 = new int[SIZE];
int[] list2 = new int[SIZE];
Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter " + SIZE + " numbers.");
// Get value in list1
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++)
{
list1[i] = console.nextInt();
}
// Copy elements in list2.
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++)
{
list2[i] = list1[i];
}
// Display elements of list2.
System.out.println("Elements of list2 are: ");
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++)
{
System.out.println(list2[i]);
}
}
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ReverseArray
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int size;
Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter the size of the array: ");
size = console.nextInt();
int[] list = new int[size];
System.out.println("Enter " + list.length + " integers.");
for (int i = 0; i < list.length; i++)
{
list[i] = console.nextInt();
}
int temp;
// Reversing elements of the array.
for (int i = 0; i < list.length / 2; i++)
{
temp = list[i];
list[i] = list[list.length - i - 1];
list[list.length - i - 1] = temp;
}
System.out.println("Reverse array: ");
// Display the reverse array.
for (int i = 0; i < list.length; i++)
{
System.out.println(list[i]);
}
}
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class MaxMinElement
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int size;
Scanner console = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter the size of the array: ");
size = console.nextInt();
int[] list = new int[size];
System.out.println("Enter " + list.length + " integers.");
for (int i = 0; i < list.length; i++)
{
list[i] = console.nextInt();
}
int max = list[0];
int min = list[0];
for (int i = 1; i < list.length; i++)
{
if(list[i] > max)
{
max = list[i];
}
if(list[i] < min)
{
min = list[i];
}
}
System.out.println("Largest element: " + max
+ " Smallest element: " + min);
}
}
a. Accept elements of an array
b. Display elements of an array
c. Search the element within array given by user
d. Sort the array using bubble sort method
Write methods for all options. The methods should be static and have one parameter name of the array.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class SearchSortArray
{
static Scanner console = new Scanner(System. in );
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int size;
System.out.print("Enter the size of the array: ");
size = console.nextInt();
int[] list = new int[size];
int option;
do
{
System.out.println("Menu ");
System.out.println("1. Read Array");
System.out.println("2. Display Array");
System.out.println("3. Search an Item in Array");
System.out.println("4. Sort the Array");
System.out.println("5. Exit");
System.out.print("Select an Option : ");
option = console.nextInt();
switch (option)
{
case 1:
readArray(list);
break;
case 2:
displayArray(list);
break;
case 3:
System.out.print("Enter the number you want to search: ");
int item = console.nextInt();
int index = searchArray(list, item);
if (index == -1)
{
System.out.println("Item not found");
}
else
{
System.out.println("Item found at position " + (index + 1));
}
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("Sorted array :");
sortArray(list);
displayArray(list);
break;
}
} while (option != 5);
}
static void readArray(int[] array)
{
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++)
{
array[i] = console.nextInt();
}
}
static void displayArray(int[] array)
{
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++)
{
System.out.print(array[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
static int searchArray(int[] array, int data)
{
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++)
{
if(array[i] == data)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
static void sortArray(int[] array)
{
for (int i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < array.length -i-1; j++)
{
if(array[j] > array[j+1])
{
int temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j+1];
array[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
}
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Program to left rotate the elements of an array
In this program, we need to rotate the elements of an array towards the left by the specified number of times. In the left rotation, each element of the array will be shifted to its left by one position and the first element of the array will be added to end of the list. This process will be followed for a specified number of times.
Algorithm
-
Step 1 : Let inputArray be an array to be rotated left by n positions.
Step 2 : Print inputArray before rotation.
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(inputArray));
Step 3 : Define one temporary variable temp which will hold the first element of inputArray.
int temp;
Step 4 : First copy the first element of inputArray into temp and then shift all elements one position left. After shifting, copy back temp into inputArray as last element. Repeat this step n times.
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
temp = inputArray[0];
for (int j = 0; j < inputArray.length-1; j++)
{
inputArray[j] = inputArray[j+1];
}
inputArray[inputArray.length – 1] = temp;
}
Step 5 : Print the rotated inputArray.
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(inputArray));
Original Array:
1 2 3 4 5
Array after left rotation:
4 5 1 2 3
Program to print the duplicate elements of an array
In this program, we need to print the duplicate elements present in the array. This can be done through two loops. The first loop will select an element and the second loop will iteration through the array by comparing the selected element with other elements. If a match is found, print the duplicate element.
 In the above array, the first duplicate will be found at the index 4 which is the duplicate of the element (2) present at index 1. So, duplicate elements in the above array are 2, 3 and 8.
In the above array, the first duplicate will be found at the index 4 which is the duplicate of the element (2) present at index 1. So, duplicate elements in the above array are 2, 3 and 8.
Algorithm
- STEP 1: START
- STEP 2: INITIALIZE arr[]= {1, 2, 3, 4, 2, 7, 8, 8, 3}.
- STEP 3: PRINT "Duplicate elements in given array:"
- STEP 4: REPEAT STEP 5 to STEP 7 for(i=0; i<arr.length; i++)
- STEP 5: REPEAT STEP 6 and STEP 7 for(j=i+1; j<arr.length; j++)
- STEP 6: if(arr[i] == arr[j])
- STEP 7: PRINT arr[j]
- STEP 8: END
Program:
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Java Program to right rotate the elements of an array
In this program, we need to rotate the elements of array towards its right by the specified number of times. An array is said to be right rotated if all elements of the array are moved to its right by one position. One approach is to loop through the array by shifting each element of the array to its next position. The last element of the array will become the first element of the rotated array.
Algorithm
-
Step 1 : Let inputArray be an array to be rotated right by n positions.
Step 2 : Print inputArray before rotation.
-
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(inputArray));
Step 3 : Define one temporary variable temp which will hold the last element of inputArray.
int temp;
Step 4 : First copy the last element of inputArray into temp and then shift all elements one position right. After shifting, copy back temp as first element of inputArray. Repeat this step n times.
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
temp = inputArray[inputArray.length-1];
for (int j = inputArray.length-1; j > 0; j–)
{
inputArray[j] = inputArray[j-1];
}
inputArray[0] = temp;
}
Step 5 : Print the rotated inputArray.
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(inputArray));
Program:
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Program to find the frequency of each element in the array
In this program, we have an array of elements to count the occurrence of its each element. One of the approaches to resolve this problem is to maintain one array to store the counts of each element of the array. Loop through the array and count the occurrence of each element as frequency and store it in another array fr.
In the given array, 1 has appeared two times so its frequency be 2 and 2 has appeared four times so have frequency 4 and so on.
Algorithm
- STEP 1: START
- STEP 2: INITIALIZE arr[] ={1, 2, 8, 3, 2, 2, 2, 5, 1 }.
- STEP 3: CREATE fr[] of arr[] length.
- STEP 4: SET visited = -1.
- STEP 5: REPEAT STEP 6 to STEP 9 for(i=0;i<arr.length;i++)
- STEP 6: SET count = 1
- STEP 7: REPEAT STEP 8 for(j=i+1;j<arr.length;j++)
- STEP 8: if(arr[i]==arr[j]) then
count++
fr[j] =visited
- STEP 9: if(fr[i]!=visited) then
fr[i]=count
- STEP 10: PRINT "------------"
- STEP 11: PRINT "Element | Frequency"
- STEP 12: PRINT "-------------"
- STEP 13: REPEAT STEP 14 for(i=0;i<fr.length;i++)
- STEP 14: if(fr[i]!=visited) then
PRINT arr[i] and fr[i]
- STEP 15: PRINT "-------------"
- STEP 16: END
Program:
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Java Program to sort the elements of an array in ascending order
In this program, we need to sort the given array in ascending order such that elements will be arranged from smallest to largest. This can be achieved through two loops. The outer loop will select an element, and inner loop allows us to compare selected element with rest of the elements.
 Elements will be sorted in such a way that the smallest element will appear on extreme left which in this case is 1. The largest element will appear on extreme right which in this case is 8.
Elements will be sorted in such a way that the smallest element will appear on extreme left which in this case is 1. The largest element will appear on extreme right which in this case is 8.
Algorithm
- STEP 1: START
- STEP 2: INITIALIZE arr[] ={5, 2, 8, 7, 1 }.
- STEP 3: SET temp =0
- STEP 4: PRINT "Elements of Original Array"
- STEP 5: REPEAT STEP 6 UNTIL i<arr.length
//for(i=0; i<arr.length; i++)
- STEP 6: PRINT arr[i]
- STEP 7: REPEAT STEP 8 to STEP 9 UNTIL i<arr.length
//for(i=0; i<arr.length; i++ )
- STEP 8: REPEAT STEP 9 UNTIL j<arr.length
//for(j=i+1;j<arr.length;j++)
- STEP 9: if(arr[i]>arr[j]) then
temp = arr[i]
arr[i]=arr[j]
arr[j]=temp
- STEP 10: PRINT new line
- STEP 11: PRINT "Elements of array sorted in ascending order"
- STEP 12: REPEAT STEP 13 UNTIL i<arr.length
//for(i=0;i<arr.length;i++)
- STEP 13: PRINT arr[i]
- STEP 14: END
Program:
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Java Program to sort the elements of an array in descending order
In this program, we need to sort the given array in descending order such that elements will be arranged from largest to smallest. This can be achieved through two loops. The outer loop will select an element, and inner loop allows us to compare selected element with rest of the elements.
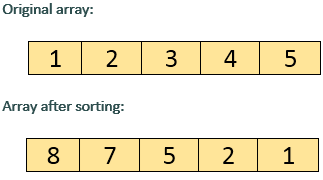 Elements will be sorted in such a way that largest element will appear on extreme left which in this case is 8. The smallest element will appear on extreme right which in this case is 1.
Elements will be sorted in such a way that largest element will appear on extreme left which in this case is 8. The smallest element will appear on extreme right which in this case is 1.
Algorithm
- STEP 1: START
- STEP 2: INITIALIZE arr[] ={5, 2, 8, 7, 1 }.
- STEP 3: SET temp =0
- STEP 4: PRINT "Elements of Original Array"
- STEP 5: REPEAT STEP 6 UNTIL i<arr.length
//for(i=0; i<arr.length; i++)
- STEP 6: PRINT arr[i]
- STEP 7: REPEAT STEP 8 to STEP 9 UNTIL i<arr.length
//for(i=0; i<arr.length; i++ )
- STEP 8: REPEAT STEP 9 UNTIL j<arr.length
//for(j=i+1;j<arr.length;j++)
- STEP 9: if(arr[i]<arr[j]) then
temp = arr[i]
arr[i]=arr[j]
arr[j]=temp
- STEP 10: PRINT new line
- STEP 11: PRINT "Elements of array sorted in descending order"
- STEP 12: REPEAT STEP 13 UNTIL i<arr.length
//for(i=0;i<arr.length;i++)
- STEP 13: PRINT arr[i]
- STEP 14: END
Program:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Java Program to find Third Largest Number in an Array
We can find the third largest number in an array in java by sorting the array and returning the 3nd largest number. Let's see the full example to find the third largest number in java array.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Java Program to find Second Largest Number in an Array
We can find the second largest number in an array in java by sorting the array and returning the 2nd largest number. Let's see the full example to find the second largest number in java array.
Find 2nd Largest Number in Array using Arrays
Let's see another example to get second largest element or number in java array using collections.
- import java.util.Arrays;
- public class SecondLargestInArrayExample1{
- public static int getSecondLargest(int[] a, int total){
- Arrays.sort(a);
- return a[total-2];
- }
- public static void main(String args[]){
- int a[]={1,2,5,6,3,2};
- int b[]={44,66,99,77,33,22,55};
- System.out.println("Second Largest: "+getSecondLargest(a,6));
- System.out.println("Second Largest: "+getSecondLargest(b,7));
- }}
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Java Program to find Second Smallest Number in an Array
We can find the second smallest number in an array in java by sorting the array and returning the 2nd element. Let's see the full example to find the second smallest number in java array.
Find 2nd Smallest Number in Array using Arrays
Let's see another example to get second smallest element or number in java array using Arrays.
- import java.util.*;
- public class SecondSmallestInArrayExample1{
- public static int getSecondSmallest(int[] a, int total){
- Arrays.sort(a);
- return a[1];
- }
- public static void main(String args[]){
- int a[]={1,2,5,6,3,2};
- int b[]={44,66,99,77,33,22,55};
- System.out.println("Second Smallest: "+getSecondSmallest(a,6));
- System.out.println("Second Smallest: "+getSecondSmallest(b,7));
- }}
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Java Program to remove duplicate element in an Array
We can remove duplicate element in an array by 2 ways: using temporary array or using separate index. To remove the duplicate element from array, the array must be in sorted order. If array is not sorted, you can sort it by calling Arrays.sort(arr) method.
1) Remove Duplicate Element in Array using Temporary Array
Remove Duplicate Element in Array using separate index
Remove Duplicate Elements in Unsorted Array
If you have unsorted array, you need to sort it first. To do so, use Arrays.sort(arr) method.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Java Program to add two matrices
We can add two matrices in java using binary + operator. A matrix is also known as array of arrays. We can add, subtract and multiply matrices.
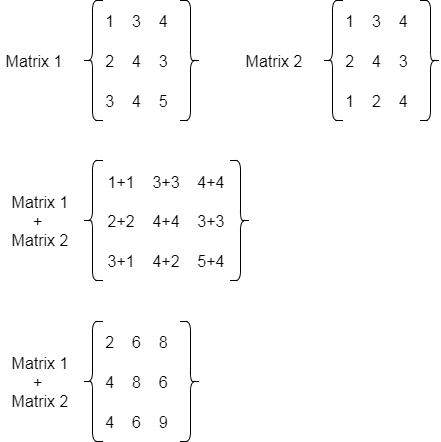 To subtract two matrices, use - operator. Let's see a simple example to add two matrices of 3 rows and 3 columns.
To subtract two matrices, use - operator. Let's see a simple example to add two matrices of 3 rows and 3 columns.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Java Program to multiply two matrices
We can multiply two matrices in java using binary * operator and executing another loop. A matrix is also known as array of arrays. We can add, subtract and multiply matrices.
In case of matrix multiplication, one row element of first matrix is multiplied by all columns of second matrix.
 Let's see a simple example to multiply two matrices of 3 rows and 3 columns.
Let's see a simple example to multiply two matrices of 3 rows and 3 columns.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Java Program to transpose matrix
Converting rows of a matrix into columns and columns of a matrix into row is called transpose of a matrix.
Let's see a simple example to transpose a matrix of 3 rows and 3 columns.
Output:Printing Matrix without transpose:
1 3 4
2 4 3
3 4 5
Printing Matrix After Transpose:
1 2 3
3 4 4
4 3 5
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Java Program to subtract the two matrices
In this program, we need to get the result of subtraction of two matrices.
Two matrices A and B can be subtracted if and only if they have same dimensions that are, the same number of rows and columns. It is not possible to subtract a 2 × 3 matrix from a 3 × 2 matrix. Subtraction of two matrices can be performed by subtracting their corresponding elements as
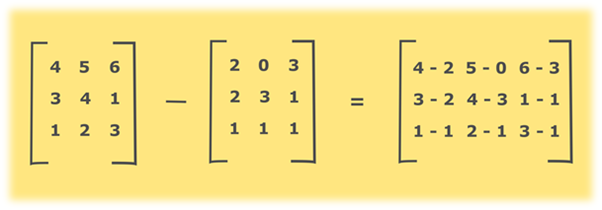 Subtraction of two matrices can be performed by looping through the first and second matrix. Calculating the difference between their corresponding elements and store the result in the third matrix.
Subtraction of two matrices can be performed by looping through the first and second matrix. Calculating the difference between their corresponding elements and store the result in the third matrix.
Algorithm
- STEP 1: START
- STEP 2: DEFINE rows, cols
- STEP 3: INITIALIZE first matrix a[][] ={{4,5,6},{3,4,1}, {1,2,3}}
- STEP 4: INITIALIZE second matrix b[][] ={{2,0,3}, {2,3,1}{1,1,1}}
- STEP 5: rows = a.length
- STEP 6: cols = a[0].length
- STEP 7: DEFINE diff[][]
- STEP 8: REPEAT STEP 9 to STEP 10 UNTIL i<rows
//for(i=0;i<rows; i++)
- STEP 9: REPEAT STEP 10 UNTIL j<cols
//for(j=0;j<cols; j++)
- STEP 10: diff[i][j] =a[i][j] - b[i][j]
- STEP 11: PRINT "Subtraction of two matrices:"
- STEP 12: REPEAT STEP 13 to STEP 14 UNTIL i<rows
//for(i=0;i<rows; i++)
- STEP 13: REPEAT STEP 14 UNTIL j<cols
//for(j=0; j<cols; j++)
- STEP 13: PRINT diff[i][j]
- STEP 14: PRINT new line
- STEP 15: END
Program:
Output:
Subtraction of two matrices:
1 5 3
1 1 0
0 1 2
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Java Program to determine whether a given matrix is an identity matrix
In this program, we need to check whether the given matrix is an identity matrix.
Identity Matrix
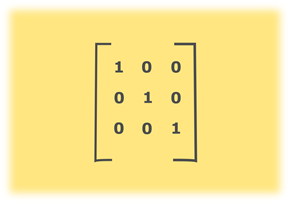 A matrix is said to be an identity matrix if it is a square matrix in which elements of principle diagonal are ones, and the rest of the elements are zeroes.
A matrix is said to be an identity matrix if it is a square matrix in which elements of principle diagonal are ones, and the rest of the elements are zeroes.
Algorithm
- STEP 1: START
- STEP 2: DEFINE rows, cols
- STEP 3: SET flag =true
- STEP 4: INITIALIZE matrix a[][] ={{1,0,0},{0,1,0}, {0,0,1}}
- STEP 5: rows = a.length
- STEP 6: cols = a[0].length
- STEP 7: if(rows!=cols)
then
PRINT "Matrix should be a square matrix"
else
go to step 8
- STEP 8: REPEAT STEP 9 to STEP 11 UNTIL i<rows
//for(i=0; i<rows; i++)
- STEP 9: REPEAT STEP 10 to STEP 11 UNTIL j<cols
//for(j=0; j<cols; j++)
- STEP 10: if(i==j && a[i][j]== 1) then
SET flag =false
break
- STEP 11: if( i!=j && a[i][j]!=0)
SET flag = false
break
- STEP 12: if(flag)
then PRINT ("Given matrix is an identity matrix")
else
PRINT ("Given matrix is not an identity matrix")
- STEP 13: END
Program:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
Java Program to determine whether a given matrix is a sparse matrix
In this program, we need to check whether the given matrix is a sparse matrix.
A matrix is said to be sparse matrix if most of the elements of that matrix are 0. It implies that it contains very less non-zero elements.
To check whether the given matrix is the sparse matrix or not, we first count the number of zero elements present in the matrix. Then calculate the size of the matrix. For the matrix to be sparse, count of zero elements present in an array must be greater than size/2.
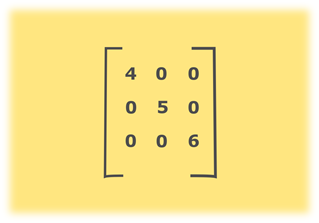 Number of zeroes present in above matrix is 6 and size of the matrix is 3 * 3 = 9. Since, 6 > 4.5 that means, most elements of given array are zero. Hence, the above matrix is a sparse matrix.
Number of zeroes present in above matrix is 6 and size of the matrix is 3 * 3 = 9. Since, 6 > 4.5 that means, most elements of given array are zero. Hence, the above matrix is a sparse matrix.
Algorithm
- STEP 1: START
- STEP 2: DEFINE rows, cols, size
- STEP 3: SET count = 0
- STEP 4: INITIALIZE first matrix a[][] ={{4,0,0}, {0,5,0}, {0,0,6}}
- STEP 5: rows = a.length
- STEP 6: cols = a[0].length
- STEP 7: size = rows*cols
- STEP 8: REPEAT STEP 9 to STEP 10 UNTIL i<rows
//for(i=0;i<rows; i++)
- STEP 9: REPEAT STEP 10 UNTIL j<cols
//for(j=0;j<cols; j++)
- STEP 10: if(a[i][j]==0) then count++
- STEP 11: if(count>size/2) then PRINT "Yes" else PRINT "No"
- STEP 12: END
Program
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Java Program to display the lower triangular matrix
In this program, we need to display the lower triangular matrix.
Lower Triangular Matrix
Lower triangular matrix is a square matrix in which all the elements above the principle diagonal will be zero. To find the lower triangular matrix, a matrix needs to be a square matrix that is, the number of rows and columns in the matrix need to be equal. Dimensions of a typical square matrix can be represented by n x n.
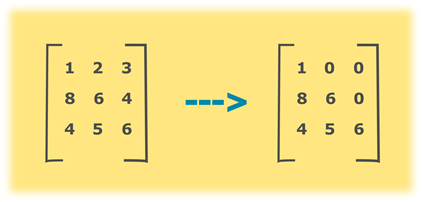 Consider the above example, principle diagonal element of given matrix is (1, 6, 6). All the elements above the diagonal needs to made zero. In our example, those elements are at positions (1, 2), (1, 3) and (2, 3). To convert given matrix into the lower triangular matrix, loop through the matrix and set the values of the element to zero where column number is greater than row number.
Consider the above example, principle diagonal element of given matrix is (1, 6, 6). All the elements above the diagonal needs to made zero. In our example, those elements are at positions (1, 2), (1, 3) and (2, 3). To convert given matrix into the lower triangular matrix, loop through the matrix and set the values of the element to zero where column number is greater than row number.
Algorithm
- STEP 1: START
- STEP 2: DEFINE rows, cols
- STEP 3: INITIALIZE matrix a[][] ={{1,2,3},{8, 6, 4}, {4, 5, 6}}
- STEP 4: rows = a.length
- STEP 5: cols = a[0].length
- STEP 6: if(rows!=cols)
then
PRINT "Matrix should be a square matrix"
else
Go to step 7
- STEP 7: REPEAT STEP 4 to STEP 6 UNTIL i<rows
//for(i=0; i<rows; i++)
- STEP 8: REPEAT STEP 9 UNTIL j<cols // for(j=0; j<cols; j++)
If(j>i) then PRINT 0 else PRINT a[i][j]
- STEP 9: PRINT new line
- STEP 10: END
Program
Output:
Lower triangular matrix:
1 0 0
8 6 0
4 5 6
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Java Program to display the upper triangular matrix
In this program, we need to display the upper triangular matrix.
Upper Triangular Matrix
Upper triangular matrix is a square matrix in which all the elements below the principle diagonal are zero. To find the upper triangular matrix, a matrix needs to be a square matrix that is, the number of rows and columns in the matrix need to be equal. Dimensions of a typical square matrix can be represented by n x n.
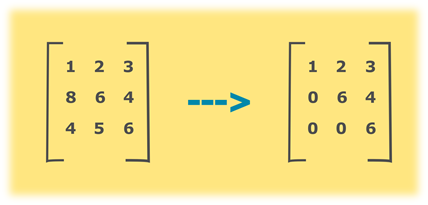 Consider the above example, principle diagonal element of given matrix is (1, 6, 6). All the elements below diagonal needs to be zero to convert it into an upper triangular matrix, in our example, those elements are at positions (2, 1), (3, 1) and (3, 2). To convert given matrix into the upper triangular matrix, loop through the matrix and set the values of the element to zero where row number is greater than column number.
Consider the above example, principle diagonal element of given matrix is (1, 6, 6). All the elements below diagonal needs to be zero to convert it into an upper triangular matrix, in our example, those elements are at positions (2, 1), (3, 1) and (3, 2). To convert given matrix into the upper triangular matrix, loop through the matrix and set the values of the element to zero where row number is greater than column number.
Algorithm
- STEP 1: START
- STEP 2: DEFINE rows, cols
- STEP 3: INITIALIZE matrix a[][] ={{1,2,3},{8, 6, 4}, {4, 5, 6}}
- STEP 4: rows = a.length
- STEP 5: cols = a[0].length
- STEP 6: if(rows!=cols)
then
PRINT "Matrix should be a square matrix"
else
Go to step 7
- STEP 7: REPEAT STEP 8 to STEP 10 UNTIL i<rows
//for(i=0; i<rows; i++)
- STEP 8: REPEAT STEP 9 UNTIL j<cols // for(j=0; j<cols; j++)
- STEP 9: If(i>j) then PRINT 0 else PRINT a[i][j]
- STEP 10: PRINT new line
- STEP 11: END
program
Output:
Upper triangular matrix:
1 2 3
0 6 4
0 0 0
How To Find All Pairs of Elements In An Array Whose Sum Is Equal To A Given Number?
public class PairsOfElementsInArray
{
static void findThePairs(int inputArray[], int inputNumber)
{
System.out.println("Pairs of elements whose sum is "+inputNumber+" are : ");
for (int i = 0; i < inputArray.length; i++)
{
for (int j = i+1; j < inputArray.length; j++)
{
if(inputArray[i]+inputArray[j] == inputNumber)
{
System.out.println(inputArray[i]+" + "+inputArray[j]+" = "+inputNumber);
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
findThePairs(new int[] {4, 6, 5, -10, 8, 5, 20}, 10);
findThePairs(new int[] {4, -5, 9, 11, 25, 13, 12, 8}, 20);
findThePairs(new int[] {12, 13, 40, 15, 8, 10, -15}, 25);
findThePairs(new int[] {12, 23, 125, 41, -75, 38, 27, 11}, 50);
}
}
Output :
Pairs of elements whose sum is 10 are :
4 + 6 = 10
5 + 5 = 10
-10 + 20 = 10
Pairs of elements whose sum is 20 are :
-5 + 25 = 20
9 + 11 = 20
12 + 8 = 20
Pairs of elements whose sum is 25 are :
12 + 13 = 25
40 + -15 = 25
15 + 10 = 25
Pairs of elements whose sum is 50 are :
12 + 38 = 50
23 + 27 = 50
125 + -75 = 50
Count the number of pairs in an array having sums that are evenly divisible by a given number.
package hackerrank;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class CountPairOfSum {
private static int countPairOfSum(int[] arr, int k) {
//brute force method --time complexity o(n2)
System.out.println("Array is:"+Arrays.toString(arr));
System.out.println("");
int paircount=0;
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++) {
for(int j=i+1;j<arr.length;j++) {
if((arr[i]+arr[j])%k==0) {
System.out.println("Pair is :"+(arr[i]+","+arr[j]));
paircount++;
}
}
}
return paircount;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//int[] ar = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}; int k=5
int[] ar= {1, 3, 2, 6, 1, 2}; int k=3;
System.out.println(countPairOfSum(ar, k));
}
}
How to reverse the first half of Array?
public class revfirsthalfIntegerArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr= {10,2,5,4,6,9,5,3};
int len=arr.length;
for(int i=0; i<len/4;i++)
{
int t = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[len/2 - i - 1];
arr[len/2 - i - 1] = t;
}
for(int j=0; j<len; j++)
{
System.out.println(arr[j]);
}
}
}
What is ModeOfArray and write the code for it?
public static void modeofarray() {
int arr[] = {1,2,3,3,4,5};
int maxnumber=-1;
int maxapperance=-1;
int result=0;
for (int i=0;i<arr.length;i++) {
int count=0;
for (int j=0;j<arr.length;j++)
{
if (arr[i]==arr[j]) {
count++;
}
}
if (count > maxapperance) {
maxnumber=arr[i];
maxapperance=count;
}
}
System.out.println("+" +maxnumber);
}
What is median in array, define the logic and write the code?
public static void medianofarray() {
int arr[]= {1,2,3,4}; //array is already sorted so no need to sort again
int arr3[]= {1,2,3,4};
if (arr.length % 2 != 0) //if number of elements are odd
{
System.out.println("median of array is: " + arr[arr.length/2]);
}else {
System.out.println("median of array is: " + (arr[(arr.length/2)]+arr[(arr.length/2-1)])/2.0);
}
}
16. How to merge two array in Java?
public static void mergetwoarray() {
int arr1[]= {1,5,2,4};
int arr2[]= {5,3,8,7,9};
//sort both arrays
Arrays.sort(arr1);
Arrays.sort(arr2);
int resultarray[] = new int[arr1.length+arr2.length];
int i = 0,j = 0,k=0;
while(i<arr1.length && j<arr2.length) {
if (arr1[i]<arr2[j]) {
resultarray[k++]=arr1[i++];
}
else{
resultarray[k++]=arr2[j++];
}
}
while(i<arr1.length) {
resultarray[k++]=arr1[i++];
}
while(j<arr2.length) {
resultarray[k++]=arr2[j++];
}
for (int l=0;l<resultarray.length;l++) {
System.out.println(resultarray[l]);
}
}
How to find the leader in an Array?
An element is leader if it is greater than all the elements to its right side.
public static void leaderinarray() {
int arrl[]= {1,2,4,3,8,6,7,1};
for (int i=0;i<arrl.length;i++) {
int j;
for ( j=i+1;j<arrl.length;j++) {
if (arrl[i]<arrl[j])
{
break;
}
}
if (j==arrl.length) {
System.out.println(arrl[i]);
}
}
}
Revision :Find the second largest in an ARRAY?
public class firstsecodlargest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1,2,3,4,5,6};
int firstlargest=0;
int secondlargest=0;
int i=0;
int n= arr.length;
for (i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if (arr[i]>firstlargest){
secondlargest=firstlargest;
firstlargest=arr[i];
}
}
System.out.println(firstlargest + " " + secondlargest);
}}

No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.